What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does It Work?
The Tibial Interlocking Nail is an innovative device used in orthopedic surgery. It provides stability and support for fractured tibia bones. This technique has revolutionized the way we approach bone healing. The nail is inserted into the medullary canal of the tibia. It is then locked in place using screws, which enhance its strength.
Patients receiving this treatment often experience reduced recovery times. The design of the Tibial Interlocking Nail allows for minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. Surgeons can perform this procedure using minimally invasive techniques. The results can be impressive, but challenges remain. Not all fractures heal as expected. Certain conditions, like infection or improper alignment, can complicate recovery.
Understanding how the Tibial Interlocking Nail works is essential. It opens new doors for effective treatment. Surgeons and patients must consider various factors when evaluating this option. Not every bone injury is suitable for this method. There may be cases requiring alternative treatments. Ultimately, the goal is to achieve the best possible outcome.
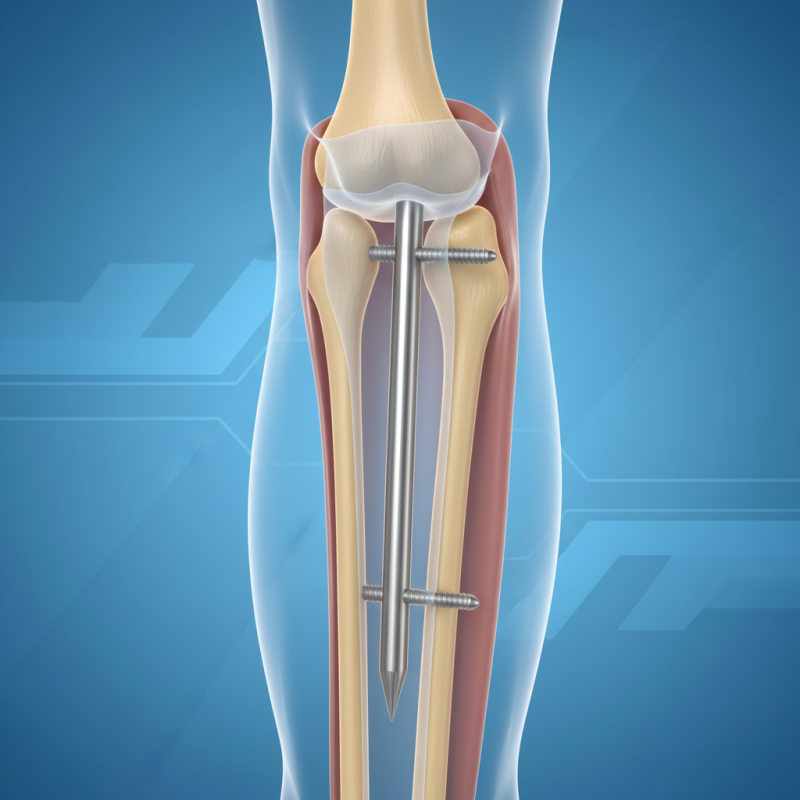
What is a Tibial Interlocking Nail?
A tibial interlocking nail is a medical device used for the stabilization of fractured tibia bones. It is a long metal rod inserted into the hollow center of the tibia. This rod is secured with locking screws that pass through the bone. The design helps facilitate healing by keeping the fractured bone segments aligned.
What makes this device effective is its ability to work in both intramedullary and extramedullary zones. The interlocking mechanism prevents rotation of the bone fragments. This feature is crucial for stability during the healing process. The procedure typically involves minimal incisions, which can lead to quicker recovery times.
Tips: Always follow the advice of your healthcare provider post-surgery. Compliance is vital. Patients may still feel discomfort or experience swelling after surgery. Managing expectations is essential for mental health.
While tibial interlocking nails are beneficial, they are not without risks. Improper insertion can lead to complications. It’s important to understand the procedure thoroughly. Consider asking your doctor about all potential risks and recovery strategies. Keeping an open line of communication is crucial for a successful outcome.
Historical Development of Tibial Interlocking Nails
The development of tibial interlocking nails has significantly shaped orthopedic surgery. These devices emerged in the 1980s as a solution for treating tibial fractures. They provided a more stable fixation than traditional methods. Clinical studies reported significantly improved outcomes, with some data suggesting a 20% reduction in non-union rates compared to conventional plates.
Early designs were limited and required extensive surgical exposure. Over time, advancements in engineering allowed for enhancements in material and design. Modern interlocking nails often incorporate locking mechanisms and varied diameters to suit different patient needs. A 2019 review indicated an 85% success rate in union for complex tibial fractures treated with this method.
However, challenges remain. Complications such as infection and malalignment still occur. Some studies indicate that 10% of patients experience these issues, necessitating further surgeries. Innovations are needed to address these shortcomings and improve long-term outcomes for patients facing tibial injuries. Continuous research and feedback from the field are crucial for future developments.
Mechanism of Action: How Tibial Interlocking Nails Function
Tibial interlocking nails have revolutionized the way we treat fractures in the tibia. These devices work by stabilizing broken bones through a minimally invasive approach. When inserted, the nail spans the fracture site, providing essential support during the healing process. Reports indicate that the success rate for fracture healing using tibial interlocking nails exceeds 90%. This highlights their effectiveness in orthopedic surgery.
The mechanism of action involves inserting the nail through the medullary canal. Once positioned, surgeons use locking bolts to secure the nail in place. This creates a stable construct, allowing for early weight-bearing activities. In fact, studies show that patients can begin partial weight-bearing as early as four weeks post-surgery. This accelerates recovery but brings challenges. Not all patients follow rehabilitation protocols effectively, leading to complications.
Moreover, complications like infection or malunion can arise. Some studies suggest that infection rates may reach 2-5%. Effective patient education is crucial to mitigate these risks. Ensuring that patients understand their role in recovery could significantly impact outcomes. Achieving optimal healing with tibial interlocking nails requires teamwork between healthcare professionals and patients.
What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does It Work?
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | Typically made from stainless steel or titanium for strength and biocompatibility. |
| Indications | Used for fractures of the tibia, particularly those that are unstable or require surgical intervention. |
| Surgical Technique | Inserted via a small incision, with the nail interlocked at both distal and proximal ends for stability. |
| Mechanism of Action | Provides internal fixation, allowing for alignment and stabilization of fractured bones during healing. |
| Recovery | Patients usually require rehabilitation and can bear weight gradually based on the healing progress. |
| Advantages | Minimally invasive, reduced healing time, good alignment, and stability. |
| Risks | Infection, non-union of the fracture, and potential need for later removal of the nail. |
Indications for Use of Tibial Interlocking Nails in Surgery
Tibial interlocking nails are used in surgery to treat fractures in the tibia, the bone in the lower leg. They provide stability and allow for better healing. These nails are particularly helpful in complex fractures, especially those that are unstable. They work by being inserted into the bone and secured with screws. This technique promotes quicker recovery.
Indications for the use of tibial interlocking nails include open fractures, severe bone loss, and cases where traditional casting is insufficient. Surgeons often choose this method when patients have high activity levels. It is effective in both adults and children. However, not every fracture is suitable for this approach. Each case needs a thorough evaluation.
Tips: When considering this procedure, patients should communicate openly with their healthcare team. Understand the risks involved. Following post-operative care instructions is crucial for healing. Keep in mind that healing can vary among individuals. Some may experience complications, while others might recover quickly. Be prepared for both possible outcomes.
Tibial Interlocking Nail Usage Indications
Potential Risks and Complications Associated with Tibial Interlocking Nails
Tibial interlocking nails are crucial for treating long bone fractures. They are effective but come with certain risks. Complications can include infection, malunion, and nonunion of the fracture site. In studies, infection rates range from 2% to 15%. These statistics underline the importance of careful surgical technique.
Another concern is the potential for hardware failure. The stress placed on these nails can lead to breakage in 3% to 5% of cases. Surgeons must weigh the benefits against these risks. Notably, patients with diabetes or compromised immune systems face higher complication rates.
Pain management is also a vital aspect. Some patients experience chronic pain post-surgery, impacting their quality of life. Surveys suggest that almost 20% feel discomfort long after healing. This highlights the need for thorough pre-operative assessments. Each patient's unique situation should guide the surgical approach and post-operative care.
© 2025 EXCELSIUS MEDICAL All rights reserved
EXCELSIUS MEDICAL
Taiwan Office
2F., No. 18, Ln.31, Sec.1, Huandong Rd.,
Xinshi Dist., Tainan City 744, Taiwan, R.O.C.
German Office
Zeppelinstr. 4, Haus 3&4,
D-85399 Hallbergmoos, Germany
